The Ungirkora cave (ungir means "cave" and kora means "yard, fold" in Kazakh) is a natural rock cavity in the Altyn-Emel National Park which presumably served as a refuge for primitive people in the Stone Age.
Anthropological Landmark
Ungirkora is the largest cave discovered in the mountains of the Altyn-Emel National Park. The height of the Ungirkora cave reaches 20 meters, the depth is 25 meters.
Smooth walls and yurt-like space suggest a handworked surface treatment. It is assumed that the cave was used by primitive people. This is evidenced by the bones of ancient animals found in the cave. The cave became an object of interest for a group of foreign scientists, searching for the sites of primitive people in Kazakhstan.
Other names for the cave are Ungirtas ("cave stone"), or Kashá ("shed" in Kazakh).
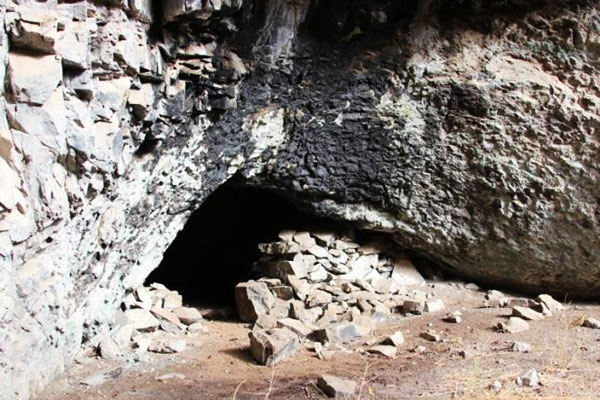

Ungirkora cave in the Altyn-Emel Park was a shelter for primitive people.

Location
The cave of Ungirkora is located in the Kaskyrsai gorge in the Sholak (Chulak) mountains, the western end of Dzhungarian Alatau.
This route is not available for tourists.
See also: